How is Carbon Fibre Made?
To better understand the role of carbon fibre weaves and how it can be used in industries from automotive to luxury bespoke furniture, it is crucial to understand the basics of how carbon fibres are formed and readied for weaving.
To create most carbon fibres, a precursor material such as PAN is subjected to stretching and pulling, transforming it into elongated, slender fibres. These are then stabilised chemically, ready for carbonisation.
The stabilised fibres are then carbonised through exposure to an oxygen-deprived, high-temperature environment, typically within a furnace. The final carbon fibres undergo washing, drying, and winding onto spools ready to be made into tows.
Carbon Fibre Tows
Carbon weave types start with bundles of carbon fibres called tows, which are rated by their filament content (3k, 6k, 12k, and 15k). The "k" stands for "thousand", indicating that a 3k tow consists of 3,000 carbon filaments. The abundance of fibres within a small space accounts for the exceptional strength-to-weight ratio of carbon fibre.
Given that each carbon fibre strand is only 5-10 microns thick, a 3k tow typically measures around 3mm in thickness. A 6k tow is twice as thick as a 3k tow, a 12k tow is four times as thick, and so on. These tows are what are then weaved into carbon fibre fabric.
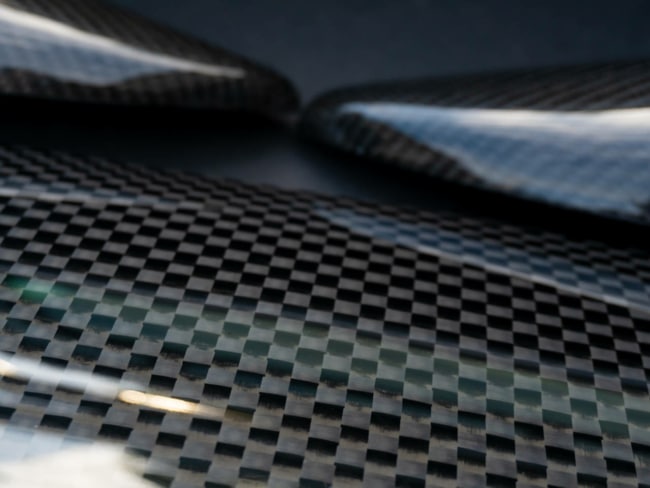

Different Carbon Fibre Weaves
There are different types of carbon fibre weave patterns to be aware of to ensure you choose one that is right for your product.
Plain Weave
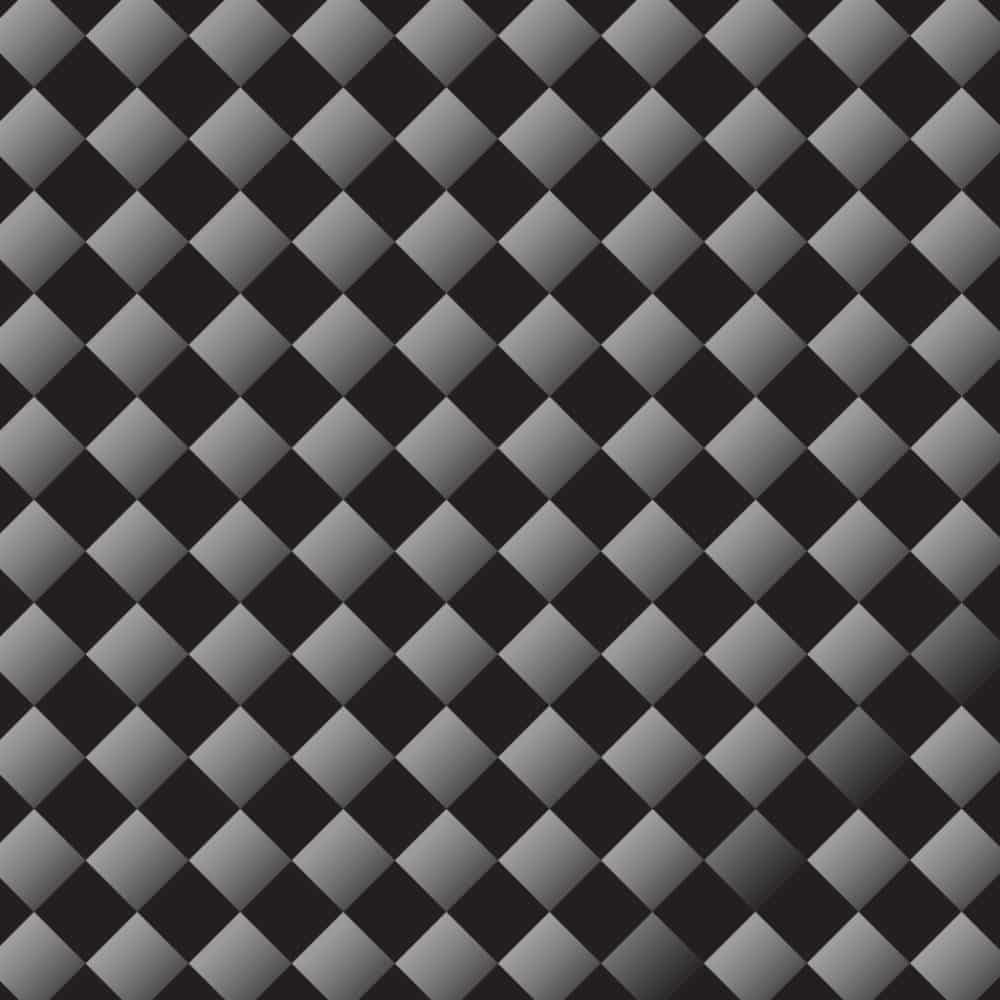
The plain weave is also known as the 1x1 weave. The tows are stitched into the fabric with an under/over motion, which creates stable tightly laced fibres and appears like a checkerboard.
Due to the weave being so tight, it isn’t appropriate for curved contours. Yet, it is easy to handle and highly durable.
Common Uses of Plain Weave Carbon Fibre:
Carbon fibre bonnets, interior trim, and body panels such as roofs often use plain weave due to its balanced strength and aesthetics.
Phone cases, laptop shells, and sporting goods (such as bicycle frames) may feature plain weave carbon fibre for its light weight and iconic look.
Certain interior and non-structural parts in aircraft, like seat backs or cabin panels, can utilise plain weave carbon fibre for its durability and weight reduction.
Twill Weave
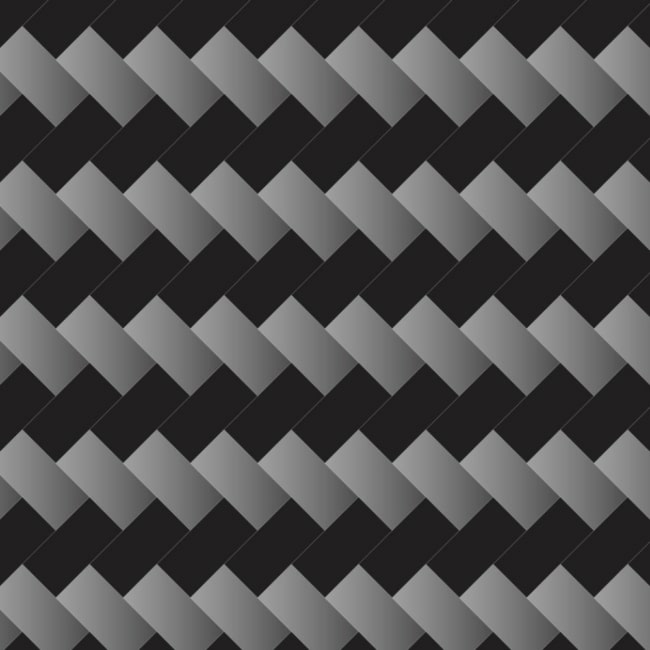
The twill weave is the most common type of carbon fibre weave pattern. Twill weave carbon fibre features a diagonal pattern created by interlacing fibres which creates a distinctive "V" shape appearance. There are different options available, including:
- 1x1 Twill
- 2x2 Twill
- 4x4 Twill
The numbers relate to the number of times the tows pass each other. For instance, the 2x2 twill weave means that the tow passes over two tows and then under two tows. For the 4x4 twill weave, the tow passes by four tows before being sewn under four tows. The 2x2 twill weave is the most common.
Common Uses of Twill Weave Carbon Fibre:
Bike frames, golf club shafts, tennis rackets, and hockey sticks often incorporate twill weave carbon fibre due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and aesthetics.
Watch cases, wallets, and sunglasses frames may utilise twill weave for its premium appearance and light weight.
Interior trims, dashboards, and motorcycle fairings sometimes feature twill weave carbon fibre to enhance the overall appeal and add a motorsport aesthetic.
Harness Satin Weave
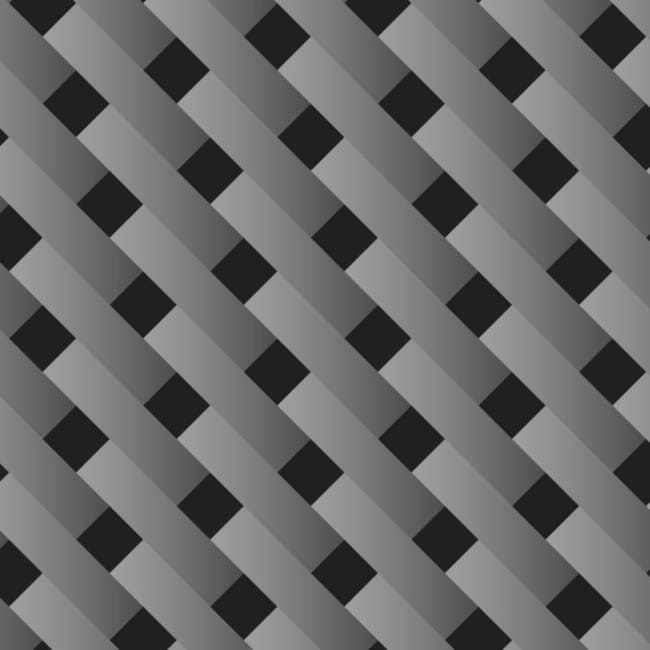
Harness satin weaves are the smoothest of them all. It has been used for multiple centuries for curving over beautiful contours.
This is highly flexible yet less stable than other types of carbon fibre weave patterns. There are several types of harness satin weaves available, including 4HS, 5HS, and 8HS (HS stands for harness satin). The higher the HS, the more flexible it is.
Common Uses of Harness Satin Weave Carbon Fibre:
Exhaust systems, engine covers, and intake manifold covers can incorporate harness satin weaves for an appearance reminiscent of motorsport.
Certain structural parts of aircraft, like winglets or fairings, may use harness satin weaves to achieve the desired balance between strength, weight, and aesthetics.
Bicycle frames, parts of snowboards or skis, and paddles for water sports may feature harness satin weaves for their combination of strength and visual appeal.
Unidirectional Carbon Fibre
The unidirectional weave pattern simply means that all fibres face in the same direction. The same direction of the stitching gives the weave pattern lots of strength and stability.
Unlike woven carbon fibre, the uni-directional option does not use interlocking tows, which means the material does not have any crimping nor the woven appearance associated with carbon fibre. Furthermore, crimping hinders the strength and durability of carbon fibre material. With no crimps, the unidirectional is a great option if you want something incredibly strong in one direction.
Common Uses of Unidirectional Carbon Fibre:
Unidirectional carbon fibre is used in aircraft wings, rocket components, and military equipment to provide maximum strength and stiffness in critical load-bearing areas.
The spar caps and leading/trailing edge reinforcements in wind turbine blades often utilise unidirectional carbon fibre for its exceptional strength and fatigue resistance.
Unidirectional carbon fibre is employed in various industrial sectors for structural reinforcements (such as in bridges) and high-performance machinery components.

Spread Tow Carbon Fibre
Spread tow is a technique that involves using a special technology to transform individual carbon fibre tows into wide and flat strands, often referred to as "tapes." For instance, a 5-mm wide carbon fibre tow is typically spread to create a 25-mm wide tape.
This process results in a fabric that is smoother and flatter compared to traditional woven fabric, with reduced crimping where the tows intersect. As a result, the spread tow fabric offers improved efficiency in carrying loads relative to its weight, as well as an enhanced surface finish.
Due to the larger scale of the weave pattern, spread tow fabric is highly effective in achieving a more prominent carbon fibre appearance, characterised by a larger and more noticeable weave pattern.
The Strongest Carbon Fibre Weave Pattern
The strongest carbon fibre weave pattern is down to opinion. The strength again is open to interpretation depending on combinations of weave, toe and manufacturing methods.
Simply put, unidirectional carbon fibre is the strongest in terms of specific weave. Yet, seeing as the tow only goes in one direction, it only has flexibility one way. On the other hand, the 2x2 twill weave offers greater flexibility both ways and offers a great level of strength for the applications it is used for.
Spread tow carbon fibre weaves can also be seen as having improved strength due to reduced effects of crimping at intersections in the weave. As mentioned above, this can result in better relative load tolerances.
What Kind of Carbon Fibre Weave Should I Use?
The perfect carbon fibre weave depends on a wide variety o f factors. Luckily, Penta Patterns are experts on working with carbon fibre and can provide advice on which to use.
Whether you wish to create bespoke furniture or components for a high performance vehicle, we will have the perfect carbon fibre to meet your needs and align with your expectations.
Do not hesitate to get in touch with us today to find out more about our range of carbon fibre weave patterns and what type will suit your product manufacturing process best.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS
Established in 1985, we have built a strong reputation for manufacturing excellent products within tight timescales and to extremely high tolerances. In order to achieve this, we use state of the art equipment and traditional, time honoured processes and skills.
Call us on:
01455 890 571
Email us at:
sales@pentapatterns.co.uk