What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing is the process of creating three-dimensional parts by adding successive layers of material to create the desired product. 3D printing services are most often associated with the term additive manufacturing, with many using the two terms interchangeably. Additive manufacturing has revolutionised various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods.
The process typically involves the following steps:
Design
The initial step is to create a 3D model of the object using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This digital model serves as the blueprint for the physical object.
Slicing
The 3D model is then divided into thin cross-sections using slicing software. Each layer is typically around 0.1 to 0.2 millimetres thick.
Preparation
The sliced model is prepared for printing by orienting it correctly and adding support structures if necessary. Support structures are temporary structures that are used to hold up overhanging or intricate parts of the object during the printing process.
Printing
The 3D printer reads the sliced model and begins the printing process, adding material layer by layer. The printer typically uses one of several additive manufacturing technologies, such as fused deposition modelling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), or selective laser sintering (SLS).
Post-processing
After printing, the object may require some post-processing steps like removal of support structures, cleaning, and surface finishing. These steps vary depending on the specific printing technology and the desired final result.
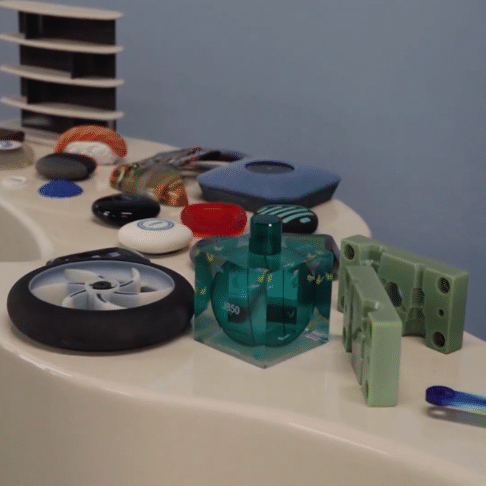

Common Materials Used in Additive Manufacturing
You can use a range of materials in additive manufacturing and 3D printing, including plastics, resins, metals, ceramics and composites. In some cases, specialised materials, such as glass, can also be used. Additive manufacturing can also be used with many recycled materials, which can make it a more environmentally friendly process.
Advantages of Additive Manufacturing
One of the major advantages of additive manufacturing is its ability to quickly create complex shapes and structures that would otherwise be difficult or even impossible to create with other manufacturing methods. Due to being created from a digital file, it has the ability to produce these objects with a higher level of detail, accuracy and repeatability than traditional methods.
Furthermore, additive manufacturing has the potential to produce parts in fewer steps than subtractive manufacturing, resulting in cost savings and reduced lead times. Additionally, it produces parts with minimal waste, which helps to reduce the environmental impact of production. Finally, it can also produce objects with a unique internal structure that is impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Products Created with Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is revolutionising the way we create products, and the possibilities are endless. Below are just a few examples :
Medical
Medical products such as prosthetics, hearing aids, and dental implants are being created with the help of this technology. During the COVID-19 pandemic, additive manufacturing was frequently utilised to rapidly produce headbands for face visors and other protective equipment.
Aerospace
Components such as airframes, turbine blades, and fuel nozzles can also be made with additive manufacturing. NASA researchers are currently investigating the performance of electroplated, 3D printed parts in space, with engineers having designed brackets that were 3D printed, then electroplated. These brackets were then sent to space on a SpaceX resupply mission to the International Space Station in 2022.
Jewellery
Designers are taking advantage of this process to bring intricate designs to life. In 2018, Indian 3D printing service, Imaginarium, created The Divine – 7801 Brahma Vajra Kamalam, a ring set with 7,801 diamonds. This broke the then world record for number of stones in one piece and demonstrated the efficacy of additive manufacturing in high-end jewellery design.
Automotive
Parts such as brake rotors, gearboxes, and suspension components can also be created using this technology. Formula 1 and motorsport in general make regular use of additive manufacturing to create prototypes and even parts to within tight tolerances - something that we at Penta Patterns are proud to be a part of.
Producing Master Patterns
The production of master patterns or master castings through additive manufacturing has helped revolutionise the practice and has found use across a variety of industries. A 3D printed master pattern can be used to then create a mould. After the mould is created, a choice of materials can be used to cast the final piece. Penta Patterns has produced pieces using this method from materials such as resin, metal and even plaster. The benefit of this process is that, although there is an initial set up cost, it allows for the creation of multiple pieces from the final mould, making small to large batch production more affordable.
Furniture
Additive manufacturing is also revolutionising the furniture industry by enabling the creation of unique pieces. With this technology, designers can bring their innovative ideas to life and produce intricate bespoke furniture designs. Our very own PolyJet 3D printing technology allows us to create complex, bespoke furniture with exceptional smoothness and detail.
What is Subtractive Manufacturing
Subtractive manufacturing, also known as subtractive processes or subtractive fabrication, is a manufacturing method where material is removed from a solid block or workpiece to create the desired shape or component. This can be done by using hand tools such as chisels, files, drills, or milling machines, or it can be achieved using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) services and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines.
Hand-operated subtractive manufacturing methods have been used for centuries, while the advent of CAD and CNC technology has revolutionised the precision and automation capabilities of this manufacturing process. CAD software enables designers to create intricate designs and produce complex geometries, which can then be executed with precision using CNC machines.
This combination of manual and digital techniques offers a range of options for manufacturers to choose from based on the complexity of the design, required precision, and desired production volume.
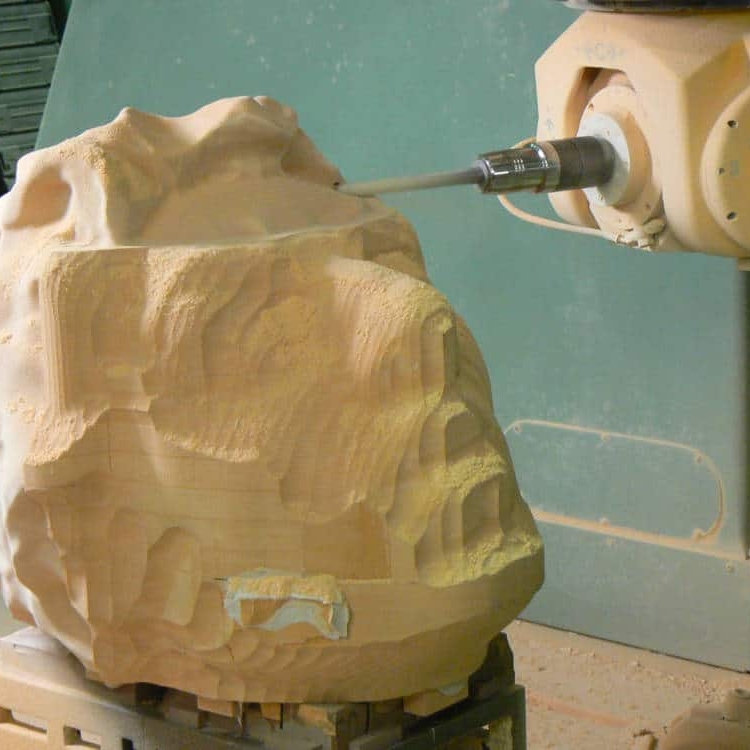
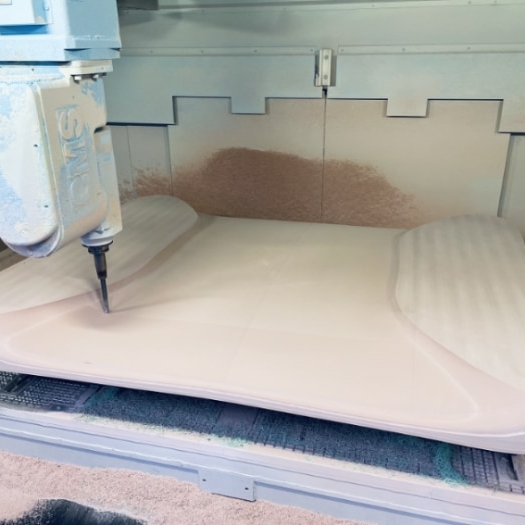


Common Materials Used in Subtractive Manufacturing
Common materials used in subtractive manufacturing include metals such as aluminium, steel, and titanium; plastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon; and ceramics like boron nitride and zirconia. Metals are usually used in machining and cutting operations, while plastics are ideal for milling and drilling. Ceramics are often used in the final stages of subtractive manufacturing processes.
The type of material used depends on the application. For example, metals are often used in medical and automotive applications, while plastics are often used in consumer products. Ceramics are often used in aerospace and military applications due to their high strength and heat resistance.
No matter what material is used, CAD subtractive manufacturing is a reliable and cost-effective way to produce components and parts. With the right materials, equipment and processes, you can create precision components and components that meet the highest quality standards.
Advantages of Subtractive Manufacturing
One of the key advantages of subtractive manufacturing is its versatility. It can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Subtractive manufacturing also offers flexibility in terms of design changes and iterations. Since material is removed from a solid block, it is easier to modify or refine the design during the manufacturing process. This allows for quick adjustments and improvements without the need for expensive tooling changes or rework.
Subtractive manufacturing can offer excellent surface finish and quality. The cutting tools used in machining processes can produce smooth and precise surfaces, free from defects or imperfections that can be found in some additive processes. This is particularly important in applications where aesthetics or functional requirements demand a high-quality surface finish.
Products Created with Subtractive Manufacturing
As mentioned, subtractive manufacturing has been around for centuries and so is found across nearly every imaginable industry. Below are just a few examples of industries that use both large and small scale subtractive processing.
Automotive
Subtractive manufacturing is extensively used in the automotive sector for various components. It involves creating engine parts, transmission components, brake system parts, and other high-precision components through milling, turning, or drilling processes. Part prototyping can also be done using CAD and CNC machines, something we regularly do at Penta Patterns.
Aerospace
Aerospace manufacturers utilise subtractive manufacturing to produce complex and lightweight parts. It is used for manufacturing turbine blades, engine components, brackets, and other critical parts that require high accuracy and precision.
Art and Sculpture
Similarly to the additive process described above, a master pattern can also be created using subtractive processes. A master pattern can be created by a CNC machine, which can be then used to create castings of the desired piece. Penta Patterns have created numerous such patterns using a combination of CNC and our 3D scanning service for use in striking sculptural pieces which were eventually cast in bronze.
Tool and Die Industry
This industry heavily relies on subtractive manufacturing for the production of moulds, dies, and other tooling equipment. The process involves milling, grinding, and other machining methods to create tools used in manufacturing processes across different industries.
Furniture Design
Subtractive manufacturing is extensively used in the furniture industry to create custom pieces and intricate designs. Wood, metal, and other materials can be cut, carved, and shaped using milling, routing and other subtractive processes to create unique and functional furniture pieces.
Architecture and Construction
Subtractive manufacturing techniques are employed in the architecture and construction industry to create precise and intricate building components. Materials such as stone, metal, or wood can be cut, shaped and sculpted using subtractive processes to produce decorative elements, intricate facades, or detailed structural components for buildings and structures.
Subtractive vs Additive Manufacturing Methods
Additive manufacturing offers greater design freedom, allowing for complex and intricate geometries that would be impossible to achieve with subtractive methods. It also opens up the possibility of producing lighter products with less material waste. However, the process can be slow and costly, and the machines require regular maintenance
Subtractive manufacturing offers faster production times and is more cost-effective in larger scale production. It also allows for the use of different materials, such as metals and composites. On the downside, it requires the use of specialised tools and can create a large amount of waste material.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS
Established in 1985, we have built a strong reputation for manufacturing excellent products within tight timescales and to extremely high tolerances. In order to achieve this, we use state of the art equipment and traditional, time honoured processes and skills.
Call us on:
01455 890 571
Email us at:
sales@pentapatterns.co.uk